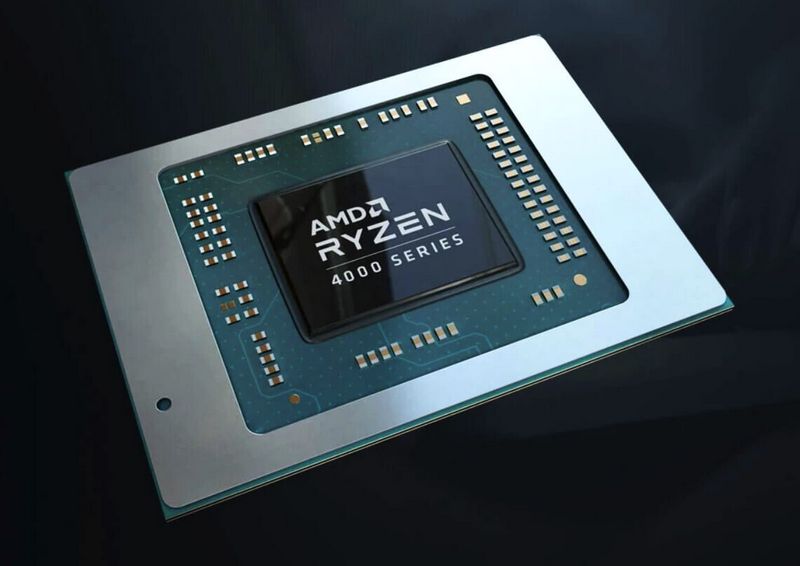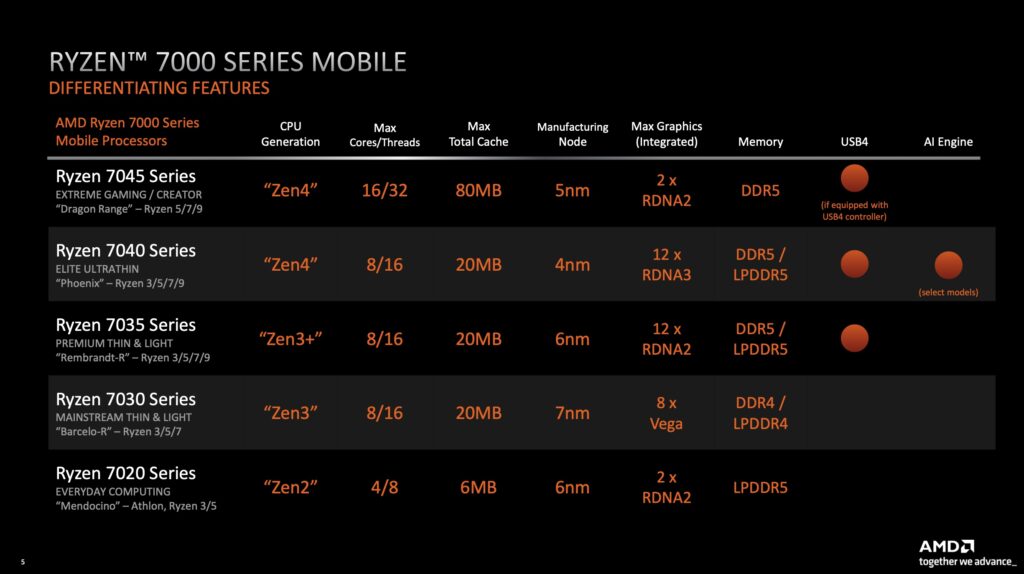
AMD said that it will replace two of its mobile Ryzen 7040U processors with a version that uses “Zen 4c” technology, an efficient CPU core that appears in AMD’s server processors and some handheld gaming chips.
“From a performance standpoint, no human will be able to tell the difference,” Don Woligroski, a senior processor technical marketing manager for AMD.
The difference, mainly, is for AMD: the core will be 35 percent smaller, saving manufacturing costs. The “replacement” Ryzens will still have the same TDP.

Including the Zen 4c technology can be seen as AMD’s answer to the “performance” and “efficiency” cores that appear in competing architectures from Arm and Intel. AMD has said previously that it has chosen to focus on performance. AMD said that combining the Zen 4 and Zen 4c cores provided the ideal combination of performance and efficiency.
Essentially, AMD is arguing that the Zen 4c cores are tuned for lowering power while maximizing efficiency across multithreaded applications. Zen 4, by contrast, will be the faster core for single-threaded, bursty applications. AMD also says that since the Zen 4 and Zen 4c cores are built on the same architecture, it doesn’t need an Intel-style thread director to route tasks to the appropriate cores, and that the operating system’s own scheduler will take care of that task.
“We haven’t done this yet, but it does give us the option to increase core counts in the future in the premium segment,” Woligroski said. “So in the future we could squeeze more cores into a processor and get higher multithreaded performance.”