5G, the fifth generation mobile network, is key in unlocking the potential of artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things, (IoT), virtual, augmented, and mixed reality, and more. The extent to which 5G will revolutionise many aspects of our lives is akin to the shift from the typewriter to the computer.
What makes 5G special compared to previous generations of mobile networks? It comes down to the differences in speed, latency, and bandwidth. 5G can be significantly faster than 4G, delivering speeds up to 10 Gigabits-per-second, while 4G tops out at 100 Megabits-per-second. Practically, 5G will allow us to download a high-resolution movie in 6 seconds at its peak download speeds. It will also essentially eliminate latency, enabling virtual interactions and conversations to be closer to real life.
More importantly, this will enable real-time remote control of automated processes (in industrial or smart city environments, for instance) that involve sensors and smart devices. Furthermore, 5G comes with increased bandwidth, which allows for greater optimisation of network traffic and smooth handling of usage spikes. We will experience seamless connectivity even in crowded areas, such as concert halls and stadiums. 5G will allow billions (if not trillions) of smart devices around the world to connect and interact among themselves, and with us.
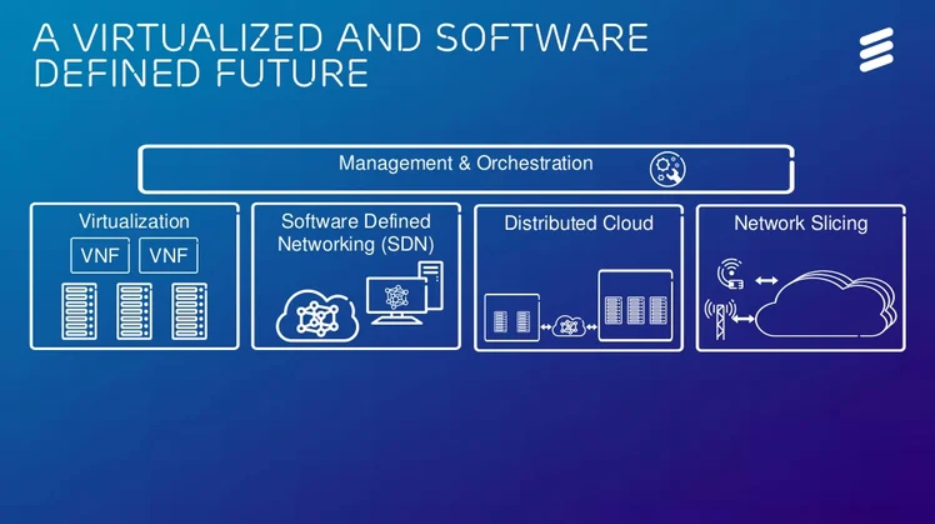
The infrastructure of 5G will look significantly different from past generations. 5G network infrastructure allows signal processing power to be moved away from transmitting ends and further into the cloud. Essentially, 5G networks can be virtualised and will open up wider market competition, as this virtualisation enables the use of end-equipments that are less technologically advanced and software solutions to operate a network. The market for 5G network infrastructure will include not only traditional telecom equipment vendors (e.g. Huawei and Ericsson), but also software-based companies such as Rakuten and Microsoft.