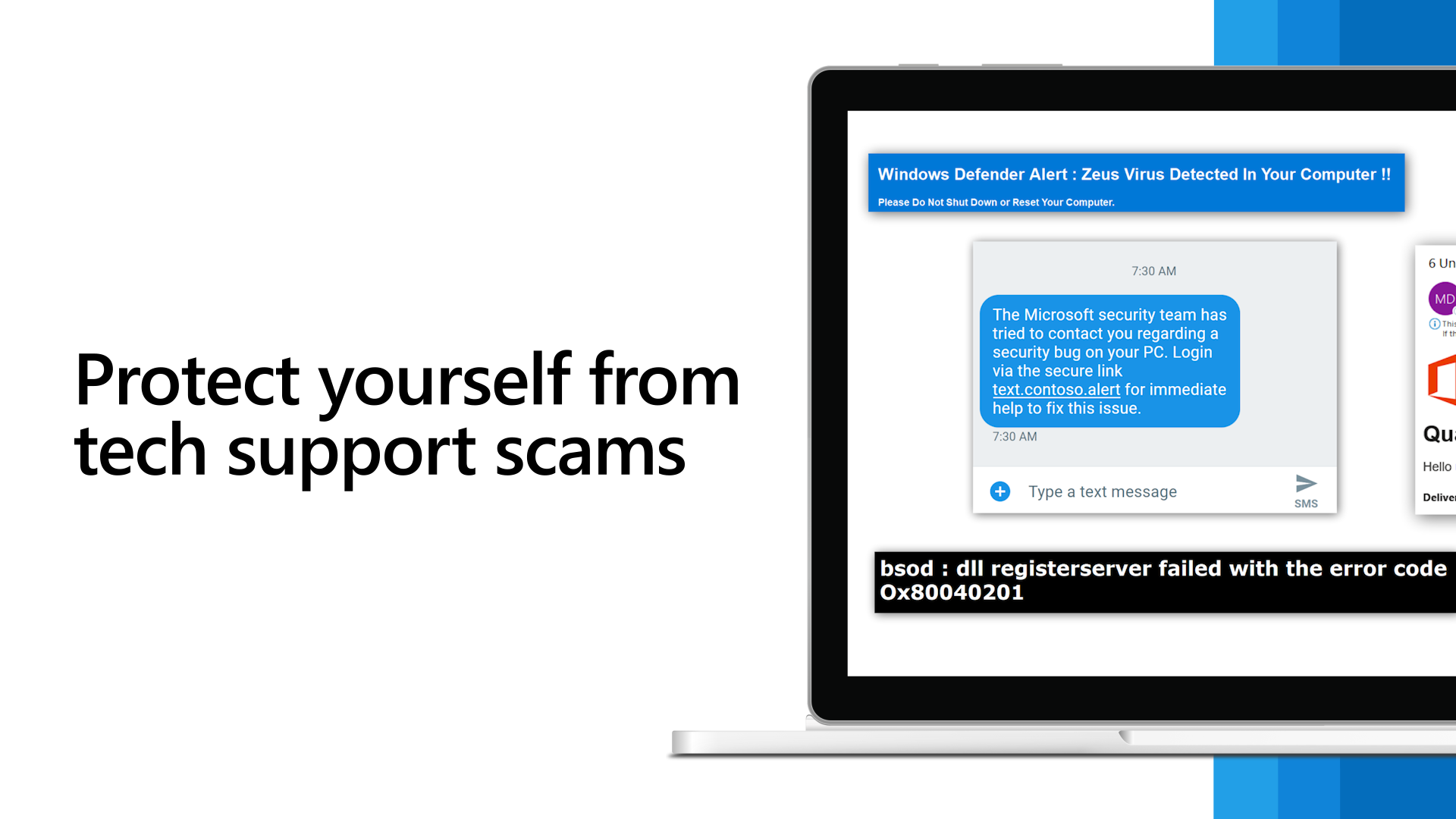
A clever yet frustrating new hacking technique is making waves in the cybersecurity community, targeting unsuspecting users to steal their Google credentials. According to a report from OALabs, attackers have found a way to exploit Chrome’s Kiosk Mode, which locks the browser into full-screen mode and restricts user navigation, creating a highly effective phishing trap.
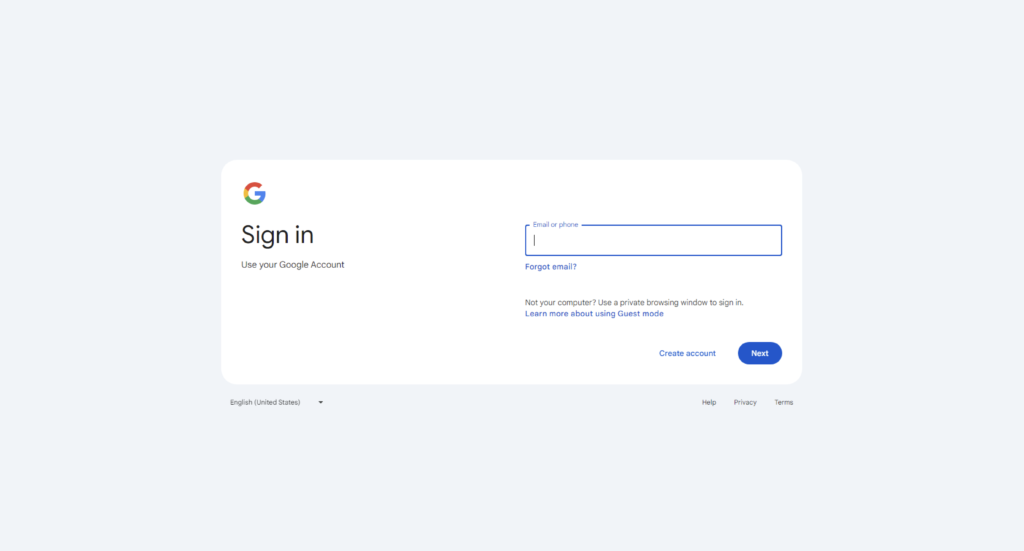
The attack begins with a Windows program that launches a counterfeit Google login page in Chrome and activates Kiosk Mode. This feature is designed for self-service kiosks, displaying content in full-screen mode while disabling certain inputs, such as the F11 key typically used to exit full-screen view. As a result, even tech-savvy users may find themselves unable to navigate away from the malicious page.
Once the user is presented with the fake login form, they are prompted to enter their Google email and password. After submission, the credentials are captured by another program that sends the data to a remote hacker. This presents a dire situation for victims, as the attacker can quickly change the account password, effectively locking the user out of Gmail and any other services linked to their Google account.
While the method has been primarily observed targeting Chrome, the underlying approach is adaptable to other browsers that implement similar Kiosk Mode functionalities. Savvy users might attempt to bypass this deceptive screen using the classic Ctrl + Alt + Delete shortcut to access the Task Manager, where they can terminate the rogue browser process. However, the simplicity and effectiveness of this tactic could easily catch even seasoned PC users off guard, leading them to unwittingly enter their credentials.
To safeguard against this type of attack, users should exercise caution when downloading software and remain vigilant about the origins of their downloads. If you encounter an unexpected full-screen Google login page, immediately attempt to exit the page and perform a thorough virus scan to check for any malicious software.