It can make sense to use your own computer as a mobile Wi-Fi hotspot, especially when you are on the road. Here’s how it works.
If your laptop has an LTE or 5G adapter and thus a fast Internet connection, you can use it as a mobile Wi-Fi hotspot to connect other devices in the vicinity to the Internet, such as your smartphone, other people’s computers.
This works with any Internet connection; your Windows laptop can also use an Ethernet connection or another Wi-Fi connection as the basis for its hotspot.
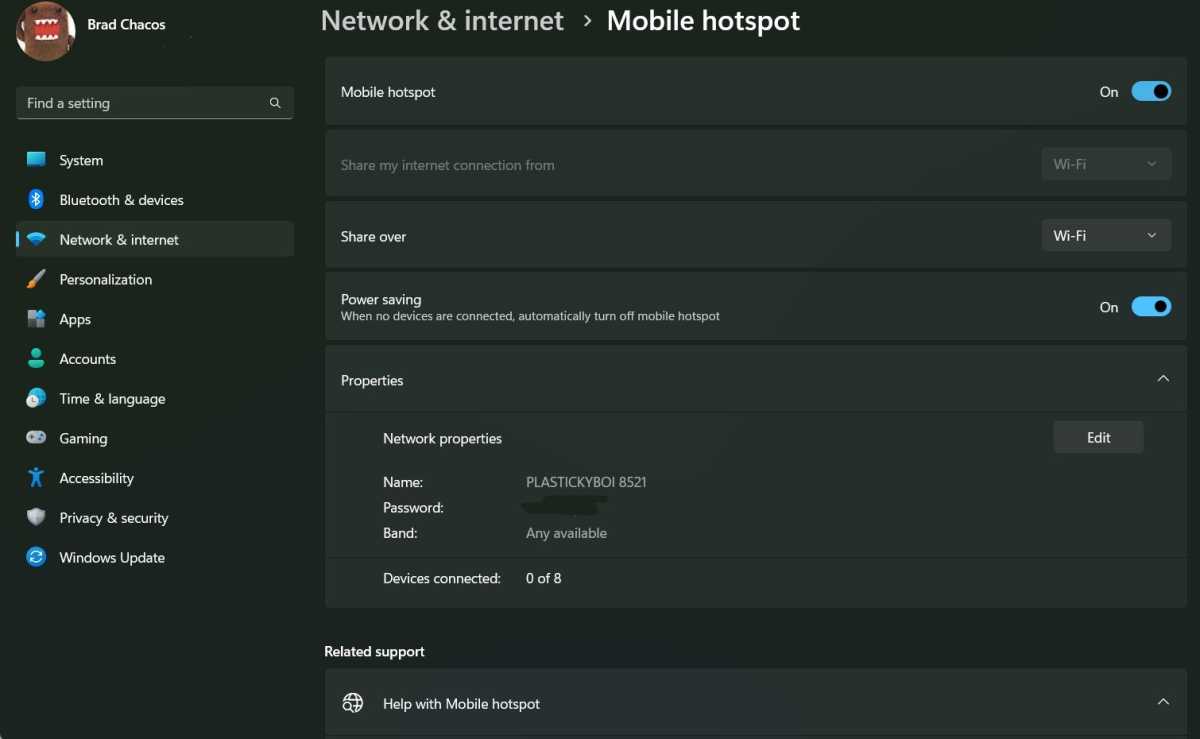
To set up the hotspot, open the “Settings” in the Windows Start menu and then “Network and Internet”. Click on the arrow pointing to the right for “Mobile Hotspot”. In the following window, set the switch to “On” and scroll down to “Properties”. Click on “Edit” if you want to change the default network name and password. Note that the password must be at least eight characters.
Brad Chacos/IDG
Laptop hotspot troubleshooting
Watch out: As soon as the hotspot is active, the option “Share own internet connection from” is greyed out and no longer accessible. If, for example, “WiFi” is set at this point and you connect an Ethernet cable, the message “No Internet connection is available, but the mobile hotspot is still on” appears. You can then access the Internet with the hosting hotspot laptop and load websites, while the hotspot broadcast from the laptop still provides access to your local network. However, there is no Internet connection via the hotspot. To get that working again, you must first deactivate the hotspot, change the setting for “Enable own internet connection from” and then reactivate the hotspot.
There are also a number of other error possibilities that can prevent the hotspot from working. For example, the Wi-Fi adapter must support hosted networks so that you can set up a hotspot.
You can check this in the command prompt. Type cmd into the search box on the taskbar, make sure “Command Prompt” is highlighted and click “Run as administrator”. Type the command netsh wlan show drivers followed by an Enter. Next look for the line “Supported hosted networks”. There should be a “Yes” behind it. If this is not the case, a hotspot cannot be set up with this adapter.
Another potential source of error is the driver for the Wi-Fi adapter. Open the Control Panel and then “Device Manager”. Now click on “Show hidden devices” under “View”. In the main window, click on the small arrow in front of “Network Adapter” and right-click on “Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Virtual Adapter”.
The adapter may not be active, in which case click on “Activate device”. You should also check the drivers: To do this, click on “Update driver” in the same context menu. Select the following windows “Search for drivers on my computer” and then “Select from a list of available drivers on my computer”. Select “Virtual Microsoft Wi-Fi Direct Adapter” and click on “Next”.